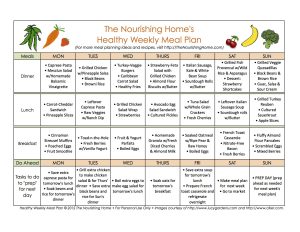
Weight loss is a topic that has garnered widespread attention in recent years. With obesity rates on the rise and the desire for a healthier lifestyle becoming more prominent, understanding the science behind weight loss is crucial. In this article, we will explore the science of weight loss and how it really works.
Caloric Deficit: The Key to Weight Loss
At its core, weight loss is achieved through a simple principle: a caloric deficit. This means that in order to lose weight, one must consume fewer calories than they burn during a day. When the body is in a caloric deficit, it begins to utilize stored fat for energy, leading to weight loss.
To achieve a caloric deficit, individuals can either reduce their calorie intake by making healthier food choices or increase their physical activity levels to burn more calories. Ideally, a combination of both strategies can produce the best results.
Metabolism and Energy Balance
The human body functions on a delicate balance of energy, which is regulated by our metabolism. Metabolism refers to the chemical processes that occur within living organisms to maintain life. It plays a vital role in determining how many calories our bodies burn at rest and during physical activity.
Metabolism can be influenced by various factors such as age, gender, genetics, and body composition. Muscle mass, for instance, has a higher metabolic rate compared to fat tissue. This means that individuals with more muscle mass naturally burn more calories, even at rest. Incorporating strength training exercises into a weight loss regimen can help boost metabolism and increase fat burning potential.
The Role of Macronutrients
While overall calorie intake is crucial for weight loss, the quality of calories consumed also matters. Macronutrients, namely carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, play different roles in the body and can impact weight loss differently.
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy and should be consumed in moderation. Simple carbohydrates, found in sugary foods and refined grains, should be limited, while complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, provide more sustained energy and essential nutrients.
Proteins are crucial for preserving muscle mass during weight loss and aiding in muscle recovery. They also contribute to increased satiety, helping individuals feel fuller for longer. Good sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and dairy products.
Fats are essential for various bodily functions and should not be completely eliminated from the diet. However, it is important to opt for healthier fats, such as those found in nuts, avocados, and olive oil, rather than saturated and trans fats found in fried and processed foods.
The Impact of Exercise on Weight Loss
Exercise goes hand in hand with a healthy diet in achieving weight loss. By engaging in physical activity, individuals can increase their caloric expenditure, further contributing to the caloric deficit necessary to shed pounds.
Cardiovascular exercises, such as jogging, cycling, or swimming, are effective in burning calories and improving cardiovascular health. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises helps build lean muscle mass, which in turn increases metabolism and facilitates weight loss.
It is important to note that weight loss is a gradual process, and sustainable results are achieved through consistency and patience. It is recommended to aim for a weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week, as this ensures healthy and lasting changes.
The Importance of Lifestyle Changes
While diet and exercise are essential components of weight loss, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in achieving long-term success. Adopting healthy habits such as proper hydration, quality sleep, stress management, and mindful eating can significantly impact weight loss outcomes.
Staying hydrated is important for overall health and can help control appetite. Adequate sleep is essential for hormonal regulation, appetite control, and maintaining energy levels. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and engaging in activities that bring joy can prevent emotional eating and promote overall well-being.
Mindful eating involves paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savoring each bite. This practice allows individuals to develop a healthier relationship with food and assists in making conscious choices that align with weight loss goals.
Conclusion
Weight loss is a journey that involves understanding the science behind it and making sustainable lifestyle changes. By creating a caloric deficit through a balanced diet and exercise, individuals can achieve gradual and lasting weight loss. It is important to focus on overall health and well-being rather than quick-fix solutions, ensuring the development of healthy habits that will benefit the body for years to come.